HN-HIP BAF summary HN - HIP BAF high efficient aeration biological filter tank, is developed and optimized on the basis of the traditional BAF technology, the modified polyurethane packing is applied, containing mixed bacterium agent. It can target different types of wastewater efficiently, can be used in the secondary biological treatment, can also be used for deep treatment. It is widely used in municipal wastewater, food, pharmaceutical, printing and dyeing, coal chemical, petrochemical and other industrial wastewater and municipal wastewater upgrading.Technical characteristics·The packing in the middle of the pool is in the semi-fluidized state on fixed bed. It can not only ensure that the outflow SS reaches the standard stably, but also solve the problem of traditional BAF packing hardening.
·Only air recoil is used, clear water or treated water back washing is not needed. The back washing volume is greatly reduced and the water yield of the system is improved.
·The packing is rich in unique and highly effective microbial agent, which can directly treat high concentration wastewater.
·There is no need of backwash fan and backwash pump. Easy to operate and maintain.Technical advantages·The biomass of the HighNew special packing is very high. It has fixing effect on bacteria.It is easy for the microorganism to stick to the membrane and not easy to be lost.
·The biomass per unit volume is large. Reliability and effluent quality is good.
·Without the foil layer, the whole packing area is full of effective organism.
·The working load is large, the volume of the pool is smaller than the traditional BAF, and there is no need to build a backwash pool.

HN-HIP BAF process diagram
Comparison Between Conventional BAF and HN-HIP BAF
| Conventional BAF | HN-HIP BAF
|
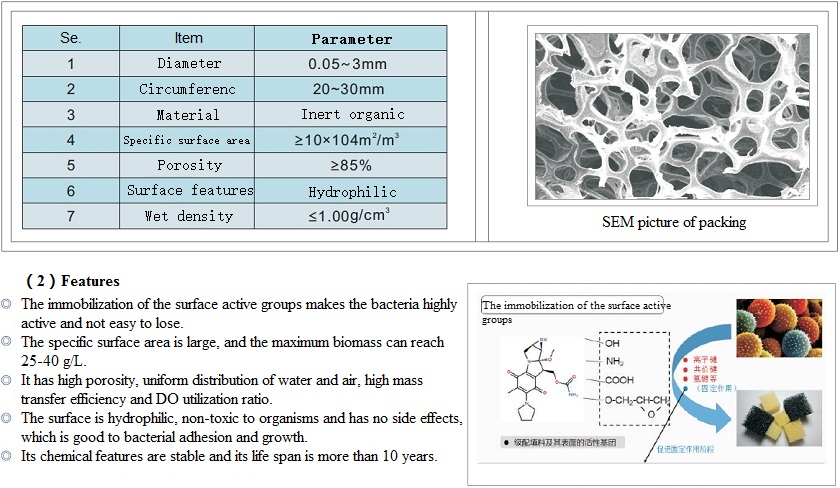
Specific surface area | Normal | High,approximately 10×104m2/m3 |
Biomass within fillers | Normal | Biomass can be between 25~40g/L |
Porosity | >36% | >85% |
Surface features | None hydrophilic | Hydrophilic with active groups on the surface |
Blocking | Easy to be blocked and requires periodically cleaning | Hardly to be blocked as the carriers are in semi-fluidization form |
Life span | Approx. 5 years | Over 10 years |
Handling | Difficult to install | Easy to install with directly pour in |
Maintenance | Difficult | Easy, carriers is in a light weight |
Supporting layer | Required | No supporting layer required (patented) |
Performance | Well | Great. With effluent BOD5≤5mg/L, NH4-N≤1mg/L. Over 95% of ammonia nitrogen can be removed. |
DO Utilization | Normal | High porosity. balanced water and air distribution. DO transmitting is highly efficient |
Back flushing | Back flush by air and water. with very high frequency | Just air flushing. No pump required. Less flushing water is consumed. At the meantime, the blower can be use for multiple purposes includes process aeration, and air scouring. Low flushing frequency: once or twice a week. |
Back flushing nozzles | Required | Not required. A perforated tube is used for back flushing |
Capital cost | High | Low, as no requirement for back flushing systems and one blower used for multi purposes. |
Back flushing tank | Required | No required |
Comparison of the operation between conventional BAF and HN-HIPBAF after years

Aeration of conventional BAF Aeration of HN- HIPBIOFILTER
HN-Compound Bacteriological Agent
(1) Function
Specific bacteria: According to the type of pollutants, different bacteria is selected and matched.
Enzyme: According to the type of bacteria, the matched enzyme is added to accelerate the biochemical reaction rate.
Bionutrients: Nutrition for bacterial growth is supplied.
(2) Characteristics
Specialized bacteria are matched according to the water quality, with strong pertinence.
The matched enzymes and nutrients are added to promote the metabolism of bacteria and accelerate the reaction speed.
The domestication time is short, which is 2/3 shorter than the traditional natural culture method.
It is non-toxic, non-corrosive and non-polluting, and no need to increase protection and safety devices.
After one-time inoculation of specific bacteria , it is not necessary to add in normal operation.
Matching of contaminants with bacteria
Se. | contaminants | Bacteria |
1 | sulfide | Thiobacillus, filamentous sulfur bacteria, photosynthetic sulfur bacteria and colorless sulfur bacteria |
2 | Benzene series | Pseudomonas fluorescens, Phenylbacillus and Bacillus |
3 | phenol | Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter Acinetobacter and Trichomonas plexus |
4 | Nitrogen compounds | Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria, nitrifying bacteria and nitrosobacteria |
5 | cyanide | Pseudomonas and Penicillium |